Our website contains links to partner sites. If you click from our site to the partner's site and purchase their services there, we will receive a commission for mediation (Find out more information). This form of cooperation does not affect the objectivity of our reviews. With each purchase made through links from our site, you support our editorial office so that we can create quality and useful content in the future. Thank you.
Important notice All our articles are written by real people. They are not artificial texts from a machine.
Uncovering VPN Vulnerability Risks: What Companies Urgently Need to Know

Lately, we’ve been witnessing increasingly frequent attacks on VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), which can seriously jeopardize the security and data of companies. How can we ensure that our corporate data remains protected? In this article, we’ll explore the vulnerabilities in VPNs and the steps we should take to effectively protect ourselves.
The Importance of VPNs in Companies
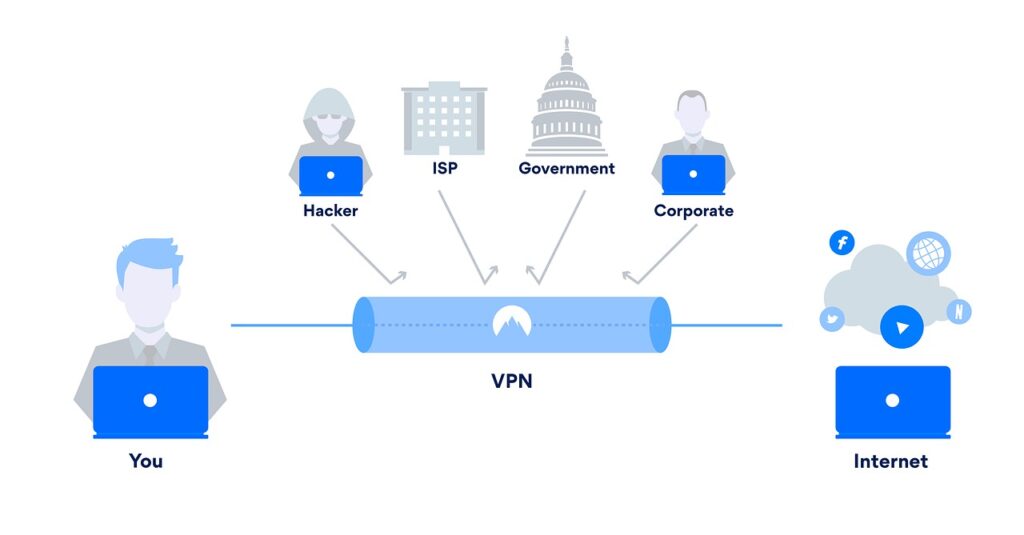
VPNs create an encrypted tunnel for data transmission, allowing employees secure access to corporate information from anywhere they work. This system has proven effective in maintaining productivity and safeguarding sensitive information during the transition to hybrid work models. Remote work gained popularity especially during the COVID-19 pandemic when companies had to quickly shift to working from home. Now, however, this work model seems to be becoming more common, and many companies already allow employees to work from home, also known as “home office.”
(Source: Pixabay.com / StefanCoders)
Given that many companies maintain a model combining work from home and from the office, VPNs are an essential tool for securing remote access. However, their vulnerabilities can open the door for cyber attackers who can easily use them to gain unauthorized access to the company network.
As the number of VPN users increases, so do the challenges associated with their security. Companies often rely on VPN software, but it can often become a security risk. The blind trust in the security of partners and suppliers is unsustainable. This situation can lead to a number of security incidents, from data breaches to extensive system disruptions.
How VPN Vulnerabilities Can Open the Doors to Cyber Attackers
- Poor Encryption: VPNs with insufficient encryption or outdated encryption protocols can allow attackers to decrypt data that is being transmitted. This can lead to the interception of sensitive information.
- Prolonged Exploitation of Outdated Software: Outdated software may contain known security flaws that have not been patched. Attackers can exploit these flaws for prolonged abuse of the system without being detected.
- Remote Code Execution (RCE): Some vulnerabilities may allow attackers to execute malicious code on servers or user devices connected to the VPN.
- DNS Leaks: VPNs should route all of a user’s internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel. However, if a DNS (Domain Name System) leak occurs, part of the traffic can escape the encrypted tunnel, allowing attackers to monitor and analyze the user’s internet activities.
- Weak Authentication Protocols: VPNs that use weak or outdated authentication protocols can be more easily breached by attackers who can then gain unauthorized access to the VPN and company network.
For companies, it is therefore crucial not only to implement VPNs as a tool for securing remote access but also to ensure that all system components are regularly updated, security policies are strictly adhered to, and employees are educated about potential threats and proper procedures for securing their digital behavior.
Identify VPN Vulnerabilities Before It’s Too Late
VPN networks are designed to provide secure access to corporate data and systems. However, they can contain weaknesses that cybercriminals exploit. One of the main vulnerabilities in VPNs is inadequate encryption, which can allow attackers to decrypt data sent through the VPN. Another issue is poor system configuration, which can lead to unintended data leaks outside the encrypted tunnel.
Another common problem is weak passwords and insufficient authentication methods, which facilitate unauthorized access.
Above all, outdated software may contain security gaps that have not been fixed in newer versions. Quality VPN providers regularly release patches and updates that address newly discovered security threats. Ignoring these updates can leave the network open to attacks and can infiltrate and damage corporate networks. Ignoring updates can lead to catastrophic scenarios, for example as one report about a threat concerning the FortiClient VPN client indicates.

Protective Measures for Securing VPN
The basic step for securing a VPN is the use of strong encryption and regular software updates. Companies should implement a security policy for strong passwords and introduce two-factor authentication for VPN access, which increases security even if the password is compromised.
Additionally, it is important to conduct regular security audits and penetration tests, which can reveal potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers, including the introduction of a supply chain verification mechanism.
In this way, companies can gain a better overview of the status of their VPN solution and effectively respond to identified issues.
Training employees should not be overlooked either. Being informed about how to recognize phishing attacks and other fraudulent activities can significantly reduce the likelihood of a security incident. Employees should be regularly informed about the best practices for using VPNs, including secure login and measures to protect their devices and data.
The Most Well-Known Security Incidents Exploiting Vulnerabilities in VPNs
In 2019, there was an attack on a VPN solution by Pulse Secure. Cyber attackers exploited a critical vulnerability that allowed them to gain administrative access without the need for authentication credentials. This vulnerability enabled attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected devices, thereby gaining deep access to the internal networks of many large corporations and government organizations.
The attackers were able to monitor and manipulate all communication passing through the compromised VPN devices. This information leak resulted in the loss of sensitive data, including personal information, corporate secrets, and other important information.
In 2020, attackers exploited a known vulnerability in Pulse Secure VPN that had not been updated in time and installed ransomware that encrypted files on the network. The attack affected the financial services company Travelex. The ransomware entered the network through an outdated VPN device. The attack paralyzed the company’s operations, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage. Moreover, Travelex had to pay a ransom and spent several weeks restoring its systems.
Also in the same year, the hacker group Clop infiltrated the internal network of the German company Software AG, encrypted files, and demanded a ransom of 20 million USD in cryptocurrency for the decryption key. Software AG refused to pay the ransom and instead collaborated with cybersecurity firms and law enforcement agencies to identify the attackers and restore its systems.
Conclusion
Although VPN systems provide key security features for remote access, they are not immune to misuse. Therefore, it is important for companies to not only implement VPN as a tool for securing remote access but also to ensure that all components of their network and security system are regularly updated and consistently monitored.
As examples of past attacks have shown, vulnerabilities in VPNs can lead to serious security incidents that can endanger not only corporate data but also the personal information of employees and customers.
In addition to technological measures, educating employees about security threats and proper practices is important, which can significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful attack. Only in this way can one effectively protect against external threats and secure valuable data and company infrastructure.









